how to naturally shrink prostate enlargement
without spending ₦15m for surgery
Experts estimate that benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) affects 5% to 6% of men ages 40 to 64 and 29% to 33% of those ages 65 and older. BPH is the most common prostate problem in men older than age 50. BPH rarely causes symptoms in men younger than age 40(national institute for diabetes and digestive and kidney diseases).
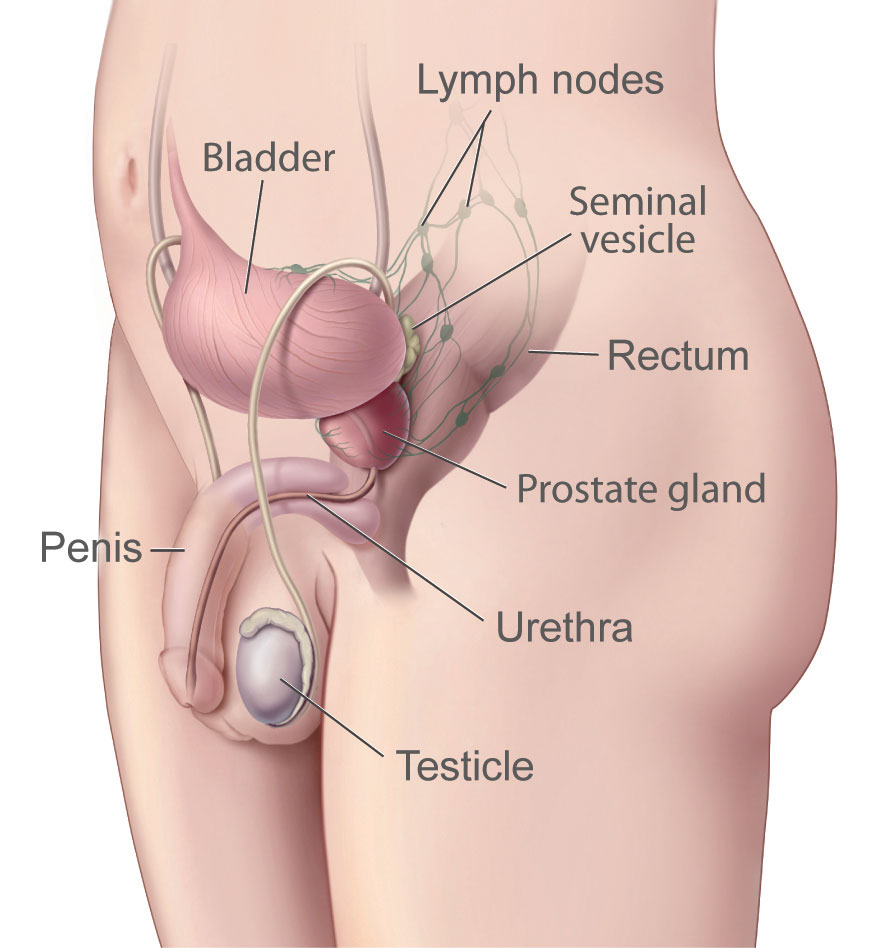
The prostate has various functions. The most important is producing seminal fluid, which is a component of semen. It also plays a role in hormone production and helps regulate urine flow. Prostate problems are common, especially in older men. The most common include an inflamed prostate, an enlarged prostate, and prostate cancer.

What is prostate?
The prostate is a small gland in men located just below the bladder and in front of the rectum. It surrounds the urethra, the tube through which urine flows. The prostate produces seminal fluid, which nourishes and transports sperm during ejaculation.
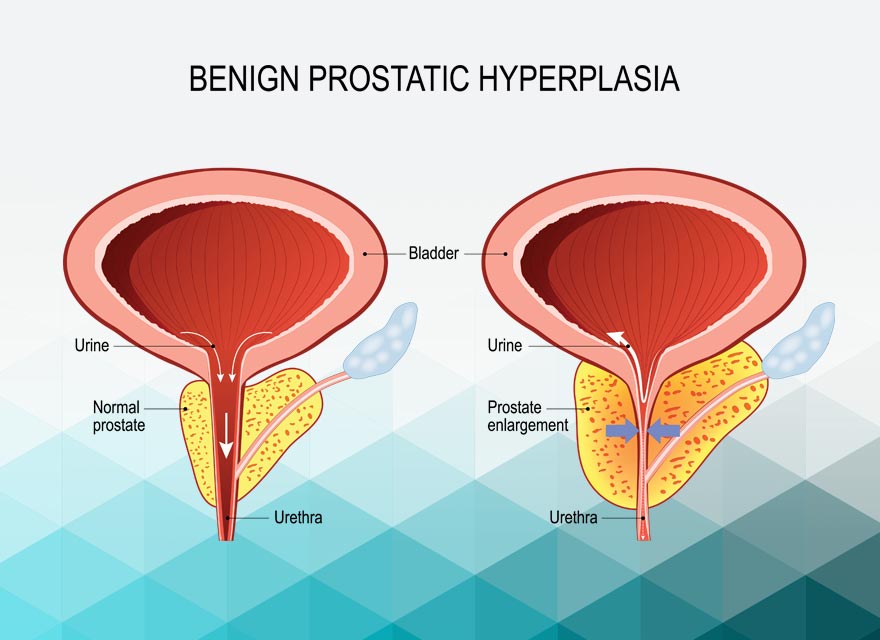
What is benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH)?
BPH commonly known as prostate enlargement is a non-cancerous enlargement of the prostate gland that commonly occurs as men age(40+). It’s not a cancer and it’s not usually a serious threat to health. It can cause urinary symptoms such as difficulty starting urination, a weak urine stream, and the need to urinate frequently.
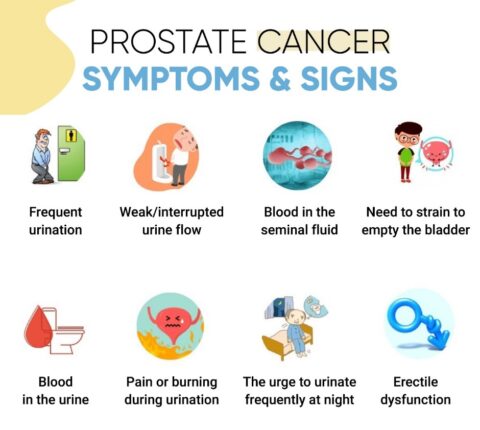
What are the common symptoms of prostate problems?
Can prostate problems affect sexual function?
Yes, prostate issues, including BPH and prostate cancer treatments, can affect sexual function. This may include erectile dysfunction and a decrease in libido. Treatment options are available to manage these issues.
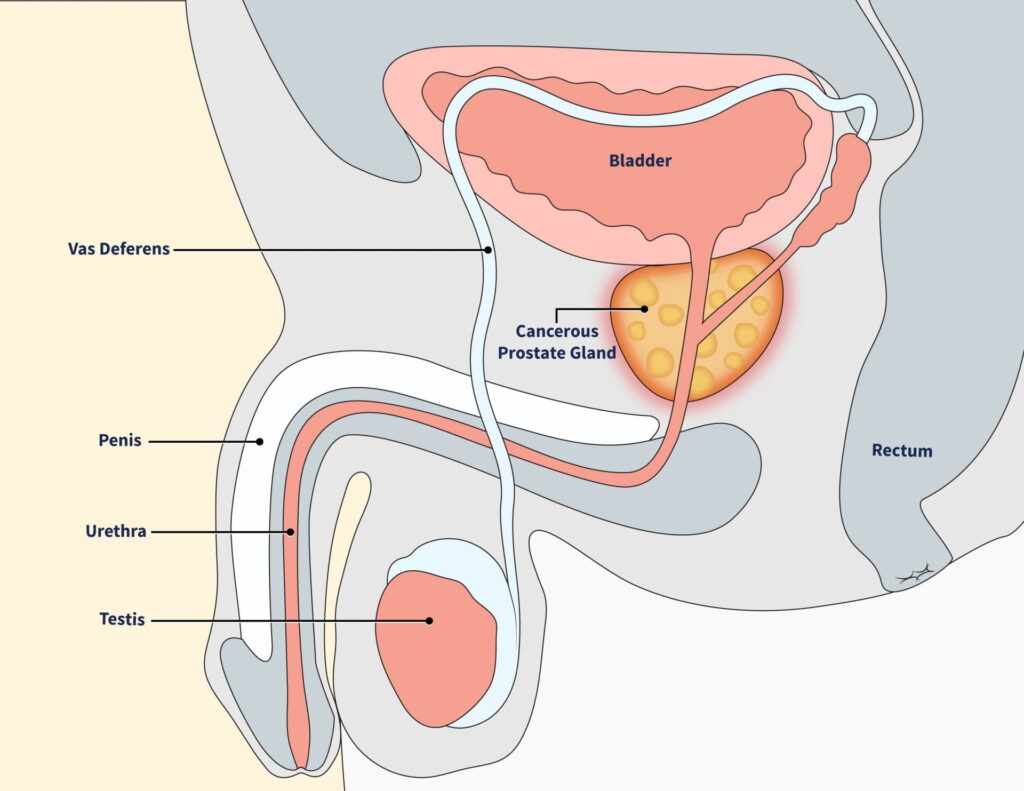
What are the complications of benign prostate enlargement?
An enlarged prostate can cause problems with emptying your bladder. As the prostate grows, it squeezes the urethra. The bladder muscles have to work harder to push urine through the narrowed urethra, which might make your urinary symptoms worse. Eventually, the bladder muscles may weaken and be unable to empty completely, leaving some urine in the bladder. This condition is called urinary retention. Other complications can include
- blood in your urine called hematuria
- urinary tract infections (UTIs)
- kidney disease
- bladder stone.
Is it possible to prevent prostate problems?
While there’s no sure way to prevent prostate problems, maintaining a healthy lifestyle can help reduce risk. This includes eating a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables, maintaining a healthy weight, exercising regularly, and avoiding smoking.
